A novel, clinical stage MSC-S therapy for potential treatment of multiple rare ocular surface diseases
KPI-012
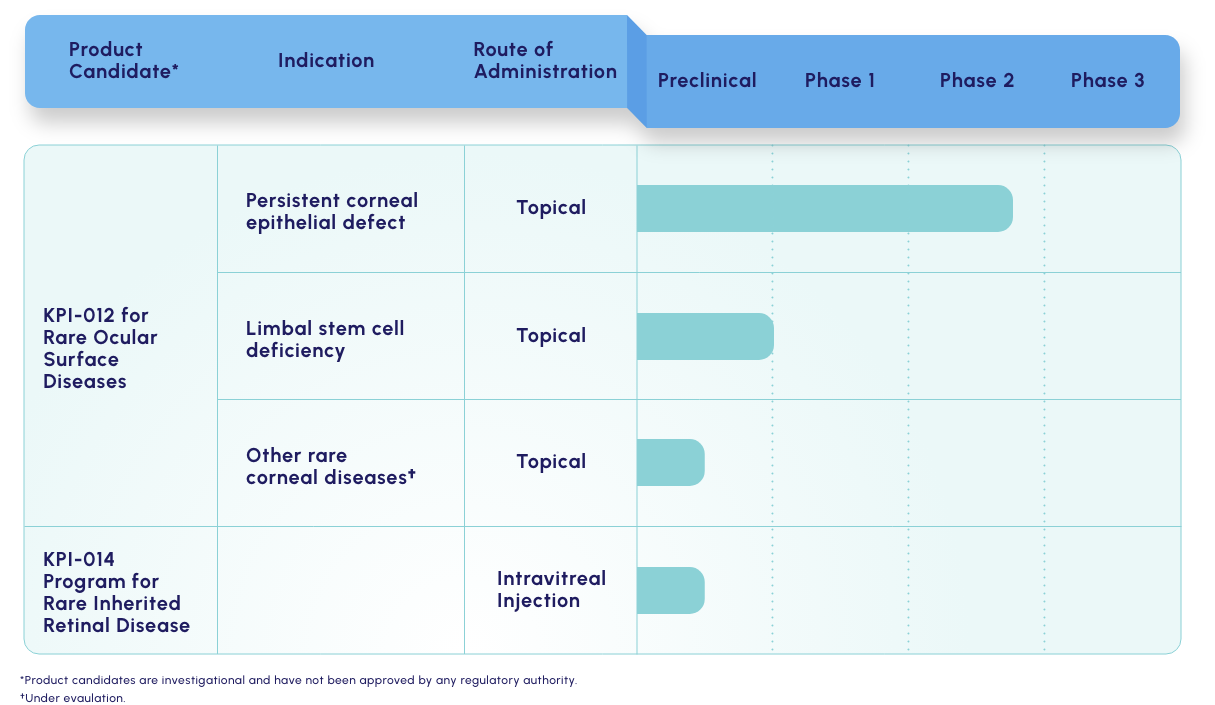
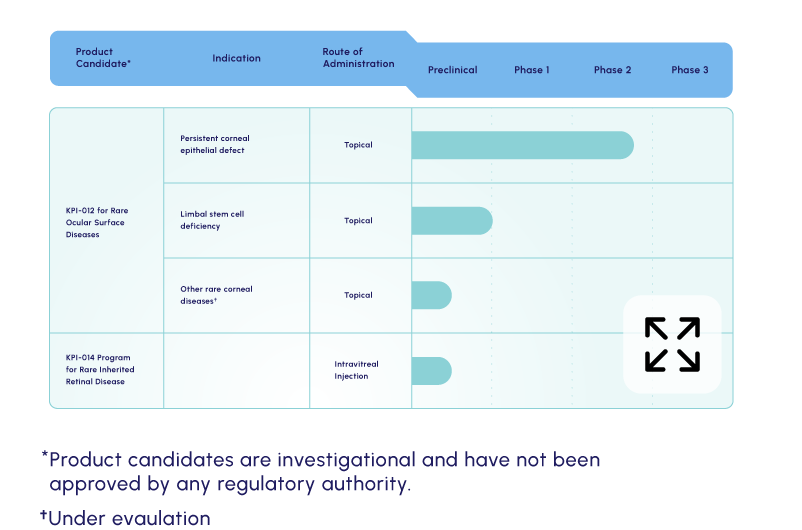
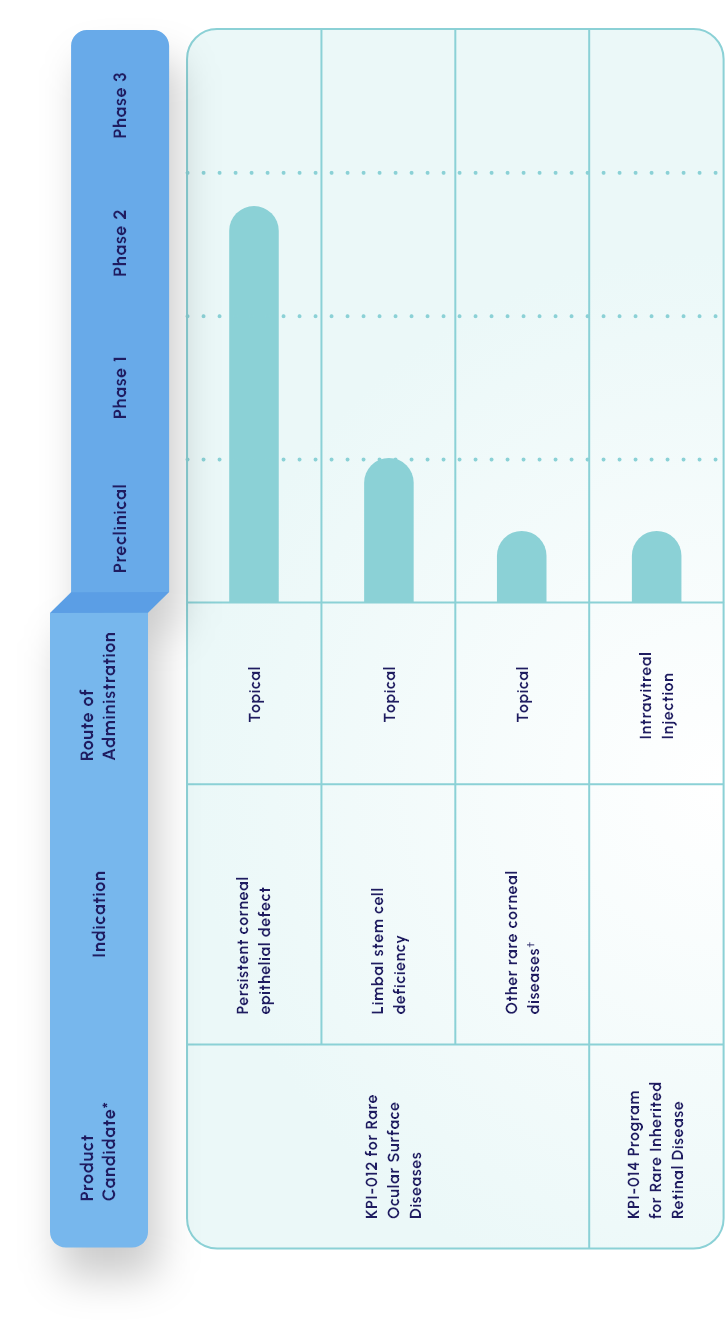
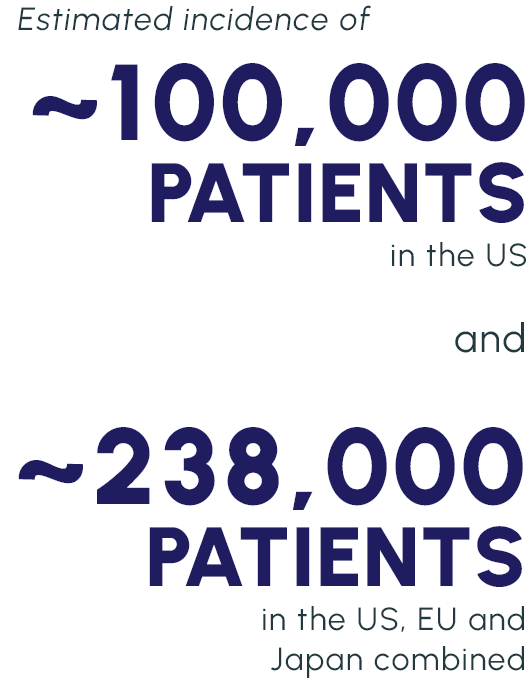
Our lead candidate is a topically dosed biologic therapy initially being developed, with FDA orphan drug and fast track designations, for the treatment of persistent corneal epithelial defect (PCED). Potential follow-on indications include limbal stem cell deficiency (LSCD) and other rare corneal diseases.
KPI-012 has been extensively characterized and contains dozens of human proteins known to facilitate normal corneal tissue repair. The key classes of KPI-012 corneal repair proteins include protease inhibitors, matrix proteins, and growth factors.
KPI-012 has the potential to be the first approved treatment for PCED with a broad indication and a differentiated product profile, potentially providing rapid and sustained wound healing, easy self-administration, and a mechanism of action that can address all etiologies.
KPI-012 is in Phase 2b development for PCED
Learn about the CHASE (Corneal Healing After Secretome Therapy) Phase 2b trial.
KPI-012 has been extensively characterized and contains dozens of human proteins known to facilitate normal corneal tissue repair. The key classes of KPI-012 corneal repair proteins include protease inhibitors, matrix proteins and, growth factors.
KPI-012 has the potential to be the first approved treatment for PCED with a broad indication addressing all etiologies, and a differentiated product profile, potentially providing rapid and sustained wound healing, easy self-administration, and a mechanism of action that can address all etiologies.
KPI-012 is in Phase 2b
development for PCED
Learn about the CHASE
(Corneal Healing After
Secretome Therapy)
Phase 2b trial.
Positive results could potentially serve as the first of two required trials to support BLA submission.
BLA, Biologics License Application.


Persistent
corneal
epithelial
defect
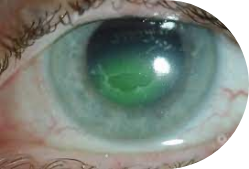
A persistent non-healing corneal defect or injury that is refractory to conventional treatments.
There are currently no FDA-approved prescription therapies with an indication for treatment of PCED across all etiologies.
Patients are at risk of infection, stromal ulceration, perforation, scarring, and permanent vision loss if defects don’t heal quickly enough.

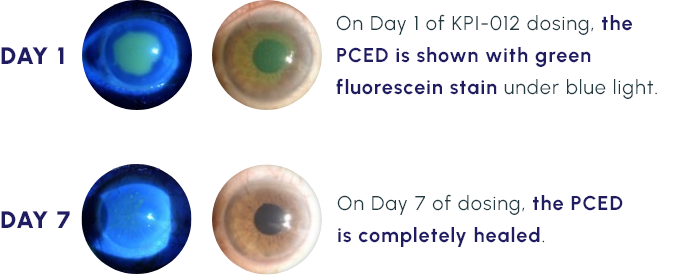
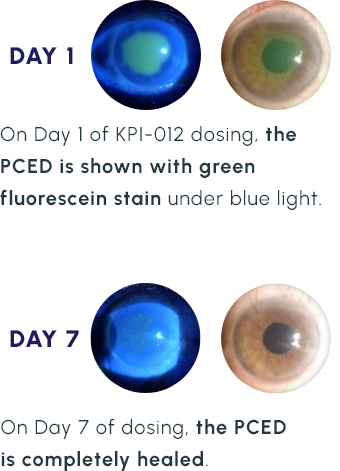
Representative Images of a KPI-012 PCED Phase 1b Study Patient Eye
Limbal
stem cell
deficiency
Loss or deficiency of limbal epithelial stem cells, which play an essential role in the generation and repopulation of corneal epithelium.
Initial treatment consists of lubricating drops, scleral lenses, amniotic membrane, and—in severe cases—surgery, including limbal stem cell transplantation.

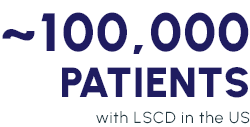
MSC-S for rare inherited retinal diseases (IRDs)
KPI-014
There is a significant need for novel therapies for slowing of disease progression in IRDs, including retinitis pigmentosa and Stargardt disease.
Over 75% of clinical pipeline assets for retinitis pigmentosa are gene-specific therapies that only target a handful of the 280 known genes associated with IRD, leaving many patients with no hope for treatment
Our KPI-014 preclinical program seeks to provide a gene-agnostic treatment for IRD by reducing progression of retinal degeneration and promoting beneficial functional outcomes.
Secretomes have demonstrated a neuroprotective effect in both in vitro and in vivo models of retinal degeneration.